Hyperion Configuration¶
We've developed a tool to automate the configuration of Hyperion. It initializes the connections with all the dependencies and creates the configuration for each chain you are running.
Warning
Check Connections Reference to add the new failover option.
Make sure you are in the installation directory:
cd ~/hyperion
Tip
Run ./hyp-config --help for more details.
Initialize connections¶
First, let's initialize our configuration. Just run:
./hyp-config connections init
Note
This command will also check the connection to Elasticsearch, Rabbitmq and Redis. Make sure everything is up and running.
You can use ./hyp-config connections test to test connectivity at any point and ./hyp-config connections reset to back up and remove the current configuration.
The initialization command will create a connections.json file that follows the template described here.
Add new chain¶
Now you can proceed and add a new chain to your configuration. Run the following command:
./hyp-config new chain eos --http "http://127.0.0.1:8888" --ship "ws://127.0.0.1:8080"
This command will create a chains/eos.config.json file that follows the template described here and also configure the state history section of the connections.json file for this chain.
Check your chain configuration¶
Finally, check your configuration running:
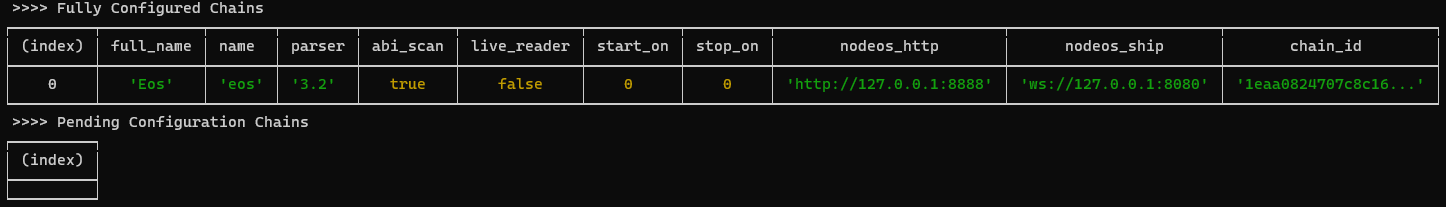
./hyp-config list chains
You should see an output similar to:
Running Hyperion¶
We provide scripts to simplify the process of starting and stopping your Hyperion Indexer or API instance.
Starting¶
To run the indexer, execute ./run.sh [chain name]-indexer
To run the api, execute ./run.sh [chain name]-api
Examples
Starting indexer for "eos" chain:
./run.sh eos-indexer
./run.sh test-api
Note
You need to pass the name of the chain you previously created followed by indexer or api to indicate the instance you want to start.
Stopping¶
Use the stop.sh script to stop an instance as follows:
Examples
Stop API for EOS mainnet:
./stop.sh eos-api
./stop.sh wax-indexer
Note
You need to pass the name of the chain you previously created followed by indexer or api to indicate the instance you want to stop.
Attention
The stop script won't stop Hyperion Indexer immediately, it will first flush the queues. Be aware that this operation could take some time.
Indexer¶
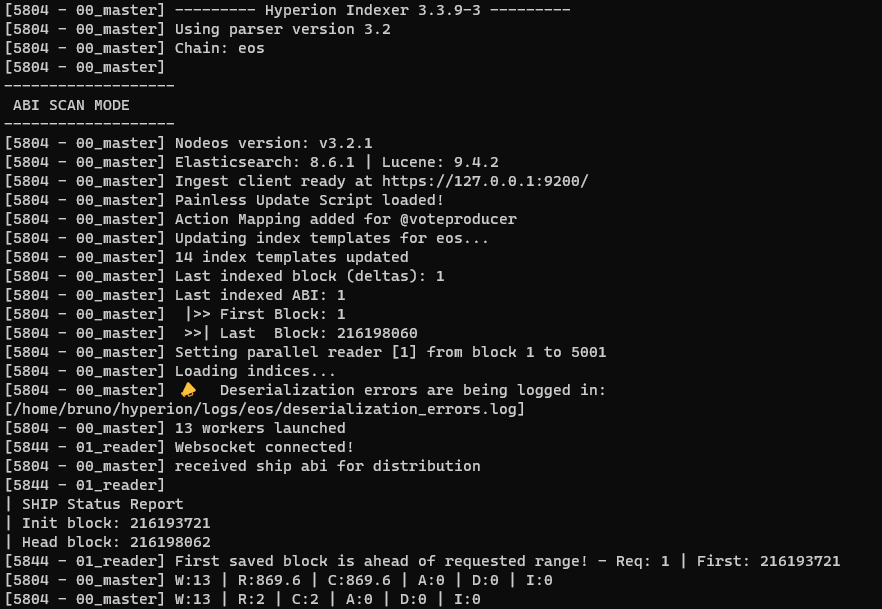
The Hyperion Indexer is configured to perform an abi scan ("abi_scan_mode": true) as default. So, on your first run,
you'll probably see something like this:
This an example of an ABI SCAN on the WAX chain.
Where:
- W (Workers): Number of workers.
- R (Read): Blocks read from state history and pushing into the blocks queue.
- C (Consumed): Blocks consumed from blocks queue.
- A (Actions): Actions being read out of processed blocks.
- D (Deserialized): Deserializations of the actions.
- I (Indexed): Indexing of all of the docs.
API¶
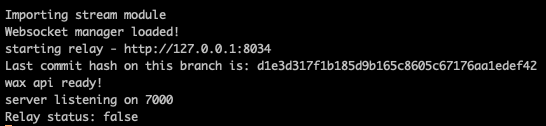
After running the api, you should see a log like this:
Now, it's time to play around making some queries.
Tip
we are using jq to format the json output for better readability
if you don't have it installed use
sudo apt install jq
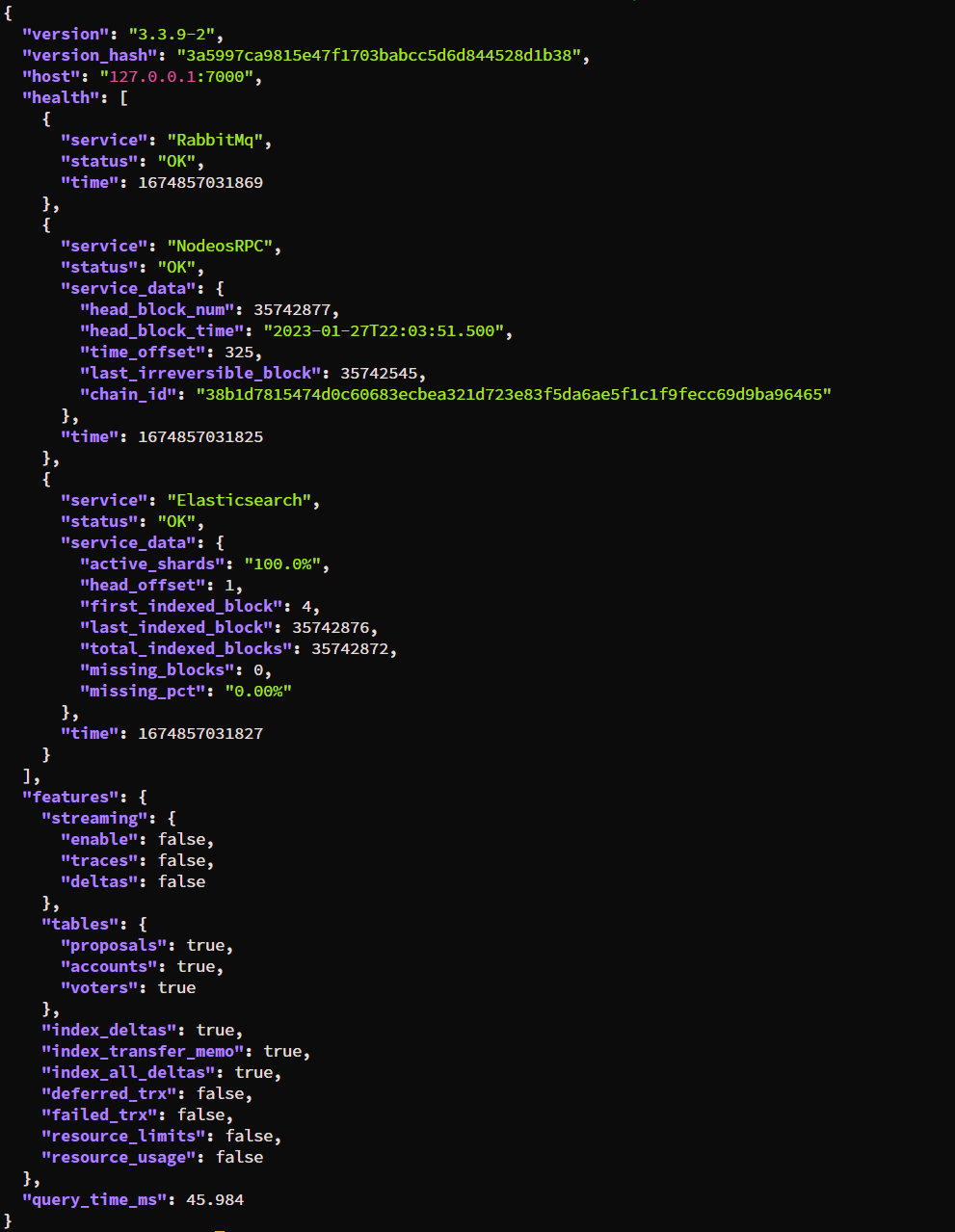
First, let's test the health check endpoint
curl -Ss "http://127.0.0.1:7000/v2/health" | jq
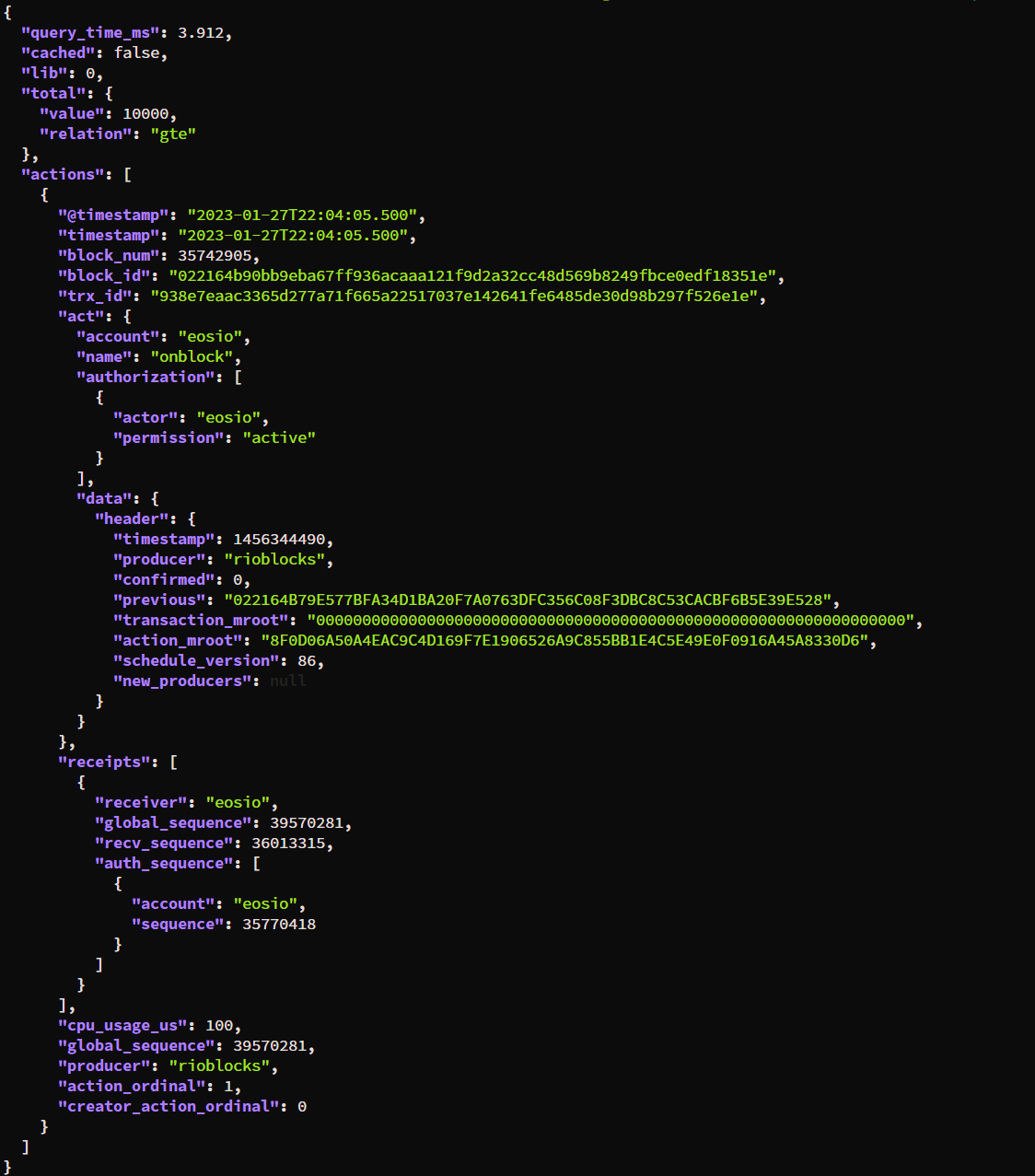
Then we can ask for the last action on chain:
curl -Ss "http://127.0.0.1:7000/v2/history/get_actions?limit=1" | jq
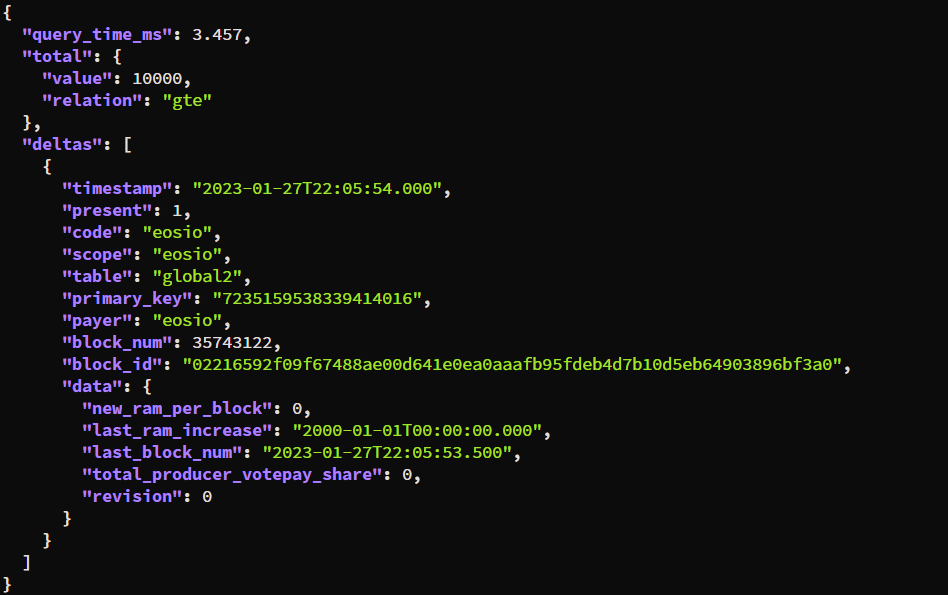
We can do the same for deltas:
curl -Ss "http://127.0.0.1:7000/v2/history/get_deltas?limit=1" | jq
You can check the Swagger UI at: http://127.0.0.1:7000/v2/docs for more information on all the available endpoints
Enabling Streaming¶
Once your indexer is finished and it's only reading live blocks, you can enable the streaming api if needed. To do so, enable all options under features.streaming in your chain config file
"features": {
"streaming": {
"enable": true,
"traces": true,
"deltas": true
}
By default, the stream api will be available on the port 1234, this can be configured by the api.stream_port property in the chain config file.
Once you're done configuring, just restart both the indexer and api.
A quick test using curl 127.0.0.1:1234/stream/ should result in the output {"code":0,"message":"Transport unknown"} meaning the port is ready for websocket connections.
Alternatively, you can check the api logs after restart for a Websocket manager loaded! message
NGINX
if you are using NGINX as your reverse proxy, use the following block to properly forward your /stream path to the correct port
location /stream/ {
proxy_set_header X-Forwarded-For $proxy_add_x_forwarded_for;
proxy_set_header Host $host;
proxy_pass http://127.0.0.1:1234/stream/;
proxy_http_version 1.1;
proxy_set_header Upgrade $http_upgrade;
proxy_set_header Connection "upgrade";
}
Finally, clients using the Hyperion Stream Client will be able to connect.
Plugins Set Up¶
Plugins are optional. Follow the documentation on the required plugin page.
Official Plugins:
Experimental Feature
Running 3rd-party plugins could be dangerous, please make sure you review the published code before installing